1.15KW BTS Solar Power System Hybrid Solar Powered Cellular Base Stations
Product Details:
| Place of Origin: | P.R.CHINA |
| Brand Name: | GPOWER |
| Certification: | CE,IEC,TUV,PSI |
| Model Number: | SOLAR POWERED BTS |
Payment & Shipping Terms:
| Minimum Order Quantity: | 1 SITE |
|---|---|
| Price: | 3999USD |
| Packaging Details: | exporting container |
| Delivery Time: | 1-2 month |
| Payment Terms: | L/C, D/P, T/T |
| Supply Ability: | 500 site per year |
|
Detail Information |
|||
| High Light: | 1.15KW BTS Solar Power System,Hybrid BTS Solar Power System,1.15KW Cellular Base Stations |
||
|---|---|---|---|
Product Description
Solar powered cellular base stations
Hybrid Solar-RF Energy for Base Transceiver Stations
The increasing deployment of cellular networks across the globe has brought two issues to the forefront: the energy cost of running these networks and the associated environmental impact. Also, most of the recent growth in cellular networks has been in developing countries, where the unavailability of reliable electricity grids forces operators to use sources like diesel generators for power, which not only increases operating costs but also contributes to pollution. Cellular base stations powered by renewable energy sources such as solar power have emerged as one of the promising solutions to these issues.
Nowadays, over two billion people, accounting for one-third of the world’s 6.6 billion population, are living without enough power supply. Africa, South America, South Asia and Southeast Asia are the main areas where power supply is inadequate. For example, in the Philippines and Indonesia, where there are numerous islands, it is impossible to build large-scale power grid covering all these small islands.
In other areas, where main high-voltage power grids are built, the power supply is not stable, and huge budget is needed to upgrade and reform the power grids. Fortunately, there are abundant renewable energy resources such as solar, wind and so on in many developing countries. It would be much more economic to widely apply power systems using renewable energy in the remote areas than construct large-area high-voltage power grids. In the regions rich in solar resources like Africa, South Asia, South East Asia, Australia, and Central America, solar power system is an ideal choice as it generates electricity to supply nearby areas and saves such costly equipment as high-voltage power grids, transformers, etc.
Power System for Remote Base Stations
Generally speaking, remote area power system consists of electricity generation, energy store, energy conversion, and management equipment. Energy generation equipment includes diesel generator, photovoltaic array, wind generator and hydraulic generator. Storage equipment includes battery pack and energy storage bank. Energy conversion and management equipment comprises DC converter and inverter switch.
Diesel generator is the main power supply in remote areas. It is necessary to keep the load at 60-70% of rated capacity to maximize fuel efficiency and reduce maintenance. The wind generator can reach 250W-500kW output; however, steady wind fields are required. Likewise, suitable and stable river current is a must for hydraulic generator. Furthermore, the hydraulic generator is expensive even though the operating cost is relatively low.
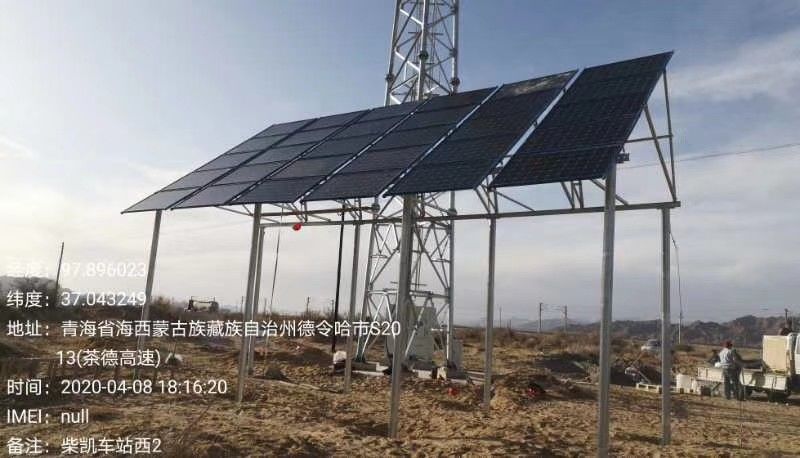
Base stations need to provide 24/7 operations. They are not only installed in urban areas, but also widely distributed in various environments such as deserts, islands, maintain tops. They are unattended, and have high demands on the reliability and lifespan of power supply. Solar photovoltaic array converts sunlight directly into electricity; powers base station equipment with 48V voltage through serial as well as parallel interconnection of photovoltaic modules. The energy conversion is static, and needs much less maintenance compared to generators relying on physical movements of mechanical parts. It is most suitable for remote area power supply system when base station site load is less than 2kW. The cost advantage of photovoltaic power system is more and more pronounced with the exhaustion of coal and oil and the continuous expansion of solar cell production.
Photovoltaic Power System for Base Station
Photovoltaic power system for base station consists of photovoltaic modules, brackets junction boxes, charge controller, battery pack and inverter and so on.
A photovoltaic module usually uses monocrystalline silicon or polycrystalline silicon cells, and a single cell has an output voltage of 0.5V. As a module is mainly composed of 72 pieces of solar cells in series, two modules should be connected serially to get output voltages ranging from 43.2V to 56.4V. Modules with relatively large capacities such as 165W, 170W and 175W are preferred. The quantity of parallel connected modules depends on load capacities and solar power resources.
Photovoltaic modules are supported by zinc coated steel brackets, which fix the modules at a certain angle. Independent photovoltaic system should be placed at an angle of 10-20 degrees higher than the latitude of the site for maximum solar radiation in winter so as to reduce the number of batteries and the cost of the whole power system.
Battery will feed loads when the solar power is not enough due to shortage of sunshine, which is common on rainy days and nights. Capacity of battery group depends on such parameters as load capacity, backup time, discharge depth, safety requirement and so on.
OPzS battery used to be the choice of solar power system as it employs positive tubular plates that can prevent the active material from falling off and thick pasted negative plates that ensure a long service life. However, OPzV with positive tubular plates gradually become popular in recent years as less maintenance is needed.
Multi-channel controller is used in charge/discharge management, and solar array is divided into several sub-arrays, which are connected to the controller via conjunction box. When battery is fully charged, the controller will cut off solar sub-arrays one by one; then battery and the rest of the photovoltaic sub-arrays provide power for the loads together. When the voltage of the battery falls to the set value, the controller will reconnect solar sub-arrays one by one to adjust the charging voltage and current of the battery.
Case Study
![]()
The electrification ratio in Indonesia has not yet achieved 100%, meaning there are still many areas without electricity access. As a key driven country development, electricity has a significant impact to the growth of telecommunication industries. In such situations, it is therefore difficult to guarantee the reliability of the telecommunication network, in particular, the electricity supply for the base transceiver station (BTS). To overcome this shortage, locally available renewable energy sources can be a solution as a power supply for a BTS. This study proposes the use of the integrated photovoltaic (PV) system as a power sources for BTS in the remote and isolated areas where the electricity from the grid is unavailable. The results show that the use of PV system is capable of supplying the electrical load requirement of BTS and is very feasible in financial analysis. The designed PV system output can produce 1.16 kW, while BTS load is 1.15 kW. We found that the integrated PV system is capable of handling BTS load. In economic perspective, the investment cost to deploy PV system is affordable due to the advantage of PV system, which is easy to maintain and operate.